- Author Lauren Nevill nevill@internetdaybook.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 18:48.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 15:15.
We often hear: "Register the DNS server", "Change the address of the DNS server", "The DNS server is not working". What is DNS? What is hidden under this abbreviation, and how significant is it in the context of the entire Internet?
Every site on the Internet has an address called an IP address. IP addresses look like: 111.111.111.111. In general, these are 4 numbers, called octets, separated by a dot. No period is needed after the last octet. Numbers can range from 0 to 255.
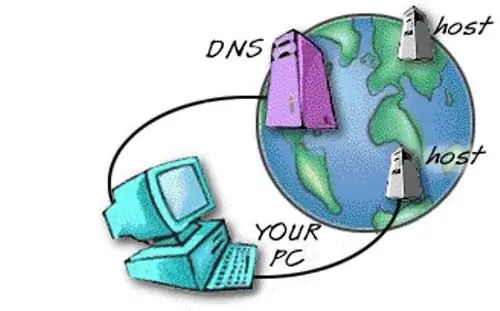
Please note that when we try to access the site, we do not type the IP address, but the domain name. For example mail.ru, yandex.ru, rambler.ru and so on. Isn't it so much easier to remember such a name than some numerical sequence?
In order to store the base of correspondence between IP addresses and domain names, the DNS (Domain Name System) system was invented. This system converts both domain names to IP addresses, and performs the reverse conversion - from an IP address to a domain name. The DNS server address can be registered in the Internet connection settings. It can be issued automatically. If the DNS server goes down for some reason, then the Internet connection will not be affected, but no domain name can be resolved to an IP address. Simply put, when typing the domain name of any site in the browser, the user will receive an error.
DNS is very important to the functioning of the entire Internet. If it were not for this system, the role of domains would essentially be abolished. There would be only IP-addresses, which are inconvenient to transfer to each other, and remembering even 1 address is much more difficult than remembering the name of the site.






