- Author Lauren Nevill nevill@internetdaybook.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 18:48.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 15:15.
On the Internet, in addition to website pages, other documents are stored and distributed. Let's take a closer look at how to upload a file to the network and place a link to it on your website.

Instructions
Step 1
You can upload a file to the server of your site using FTP (File Transfer Protocol) using a special program. Such programs are called FTP clients, and there are many of them, both paid and free. For example: FlashFXP, Cute FTP, WS FTP, FileZilla, Smart FTP, etc. After installing the program, you will need to enter your hosting details - the address of its FTP server and login with a password. Different programs organize this in different ways, but the principle is the same. The download itself is not difficult - in the left pane, along the folder tree, you need to go to the folder where the file is stored on your computer, and in the right pane - to the desired site folder, and then just drag the desired file from the left pane to the right., its mastering and setting, as you know, will require a certain amount of time. There is an alternative - you can use the file manager of your hosting control panel, which allows you to upload the necessary files directly through your browser. You just need to find where exactly the file manager is located in your control panel - unfortunately there is no single standard and the administration systems of hosting companies differ. If the file is too large, and space on your server is limited, then you can use public file storages, for example - multiupload.com. By uploading a file there, you will receive links to it, which you can place on your site in the same way as links to files on your server.
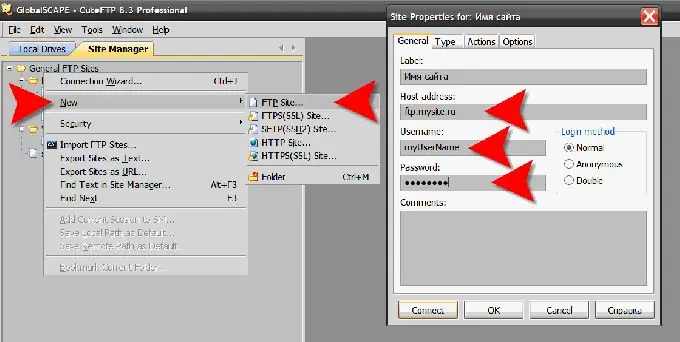
Step 2
After downloading the file, you will need to place a link to it on the desired page of the site. A link to a file in the document code is no different from a link to a regular page. It, like any other element of a web page, is rendered by the browser based on the information in the source code sent to it by the server. Source code is a set of instructions, written in HyperText Markup Language (HTML), that describe the location, type, and appearance of each element on a page. These HTML instructions are commonly referred to as "tags". The link to the file will be created by the browser when it reads the corresponding tag from the page code: Link to file In this example, this is the opening tag of the link, and the closing one. In the opening tag, you can place "attributes" - additional information about the appearance and features of the "behavior" of this tag. In this sample, the href attribute specifies the URL of the file that should be requested if a visitor clicks on the link. Such an address is called "relative" - it indicates the path to the file, measuring it from the location of the current page. If the file is located on another site, or on the same one, but in a folder one level higher than the current one, then the "absolute" address should be specified. A link with an absolute address will look, for example, like this: Link to file That is, to place a link to a file in any page of the site, you need to open the html-code of this page and add the appropriate tag in the right place. If the file with the code of the required page is at your disposal, then you can open and edit it in any text editor. If you use any of the control systems to manage your site, then you can edit the pages right in the browser. To do this, in the control panel of the system, you need to find the page editor and open the page you need in this online editor.
Step 3
As with a link to a page, you can specify other attributes in the tag of a link to a file that allow you to change the appearance and rules of its processing by the browser. The target attribute is one of the most important for this tag. It contains an indication of the window where the link should be loaded. In the HTML language, there are four options for this: _self - loading must be carried out into the same window or frame. "Frame" is one of the parts of the page if it is divided into several such parts; _parent - if the page with the link was itself loaded using scripts from another window or frame, then it has a "parent" window. The _parent value instructs to load the file pointed to by the link into this very parent window; _top - the file must be loaded into the same window, while all existing frames in it (if any) must be destroyed; _blank - requires the file to be loaded by this link opens a separate window; Sample: Upload a file in a new window






